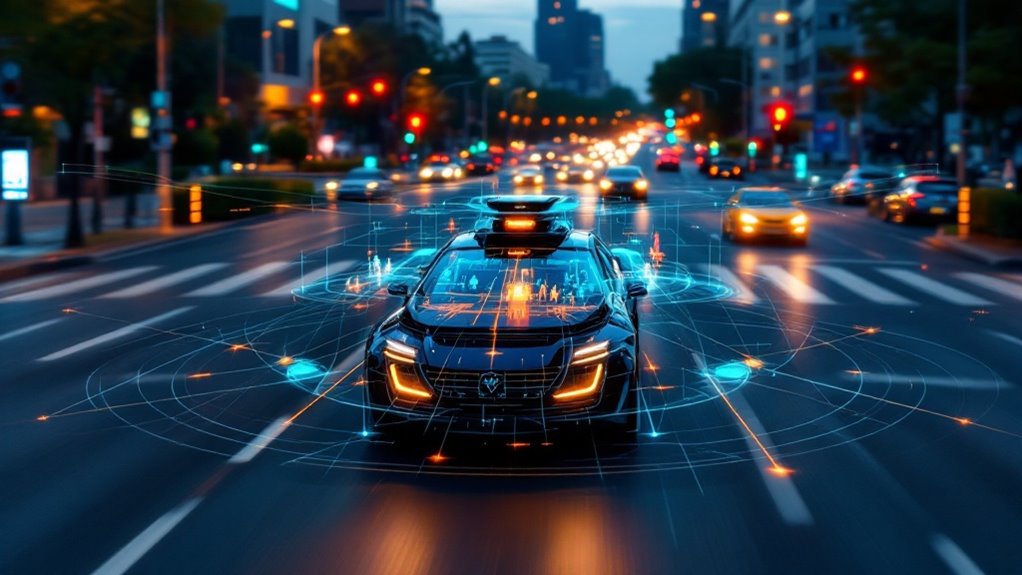
AI functions as the brain of autonomous vehicles, processing inputs from cameras, lidar, and radar to create a 360-degree understanding of surroundings. It juggles perception, decision-making, and control functions simultaneously—without needing coffee breaks. Working at lightning speed, the AI evaluates countless variables to determine ideal driving actions while predicting future events. Think Olympic-level reflexes with computer precision. The technology undergoes rigorous testing to prepare for real-world chaos you wouldn’t believe.
Beneath the sleek exteriors and whirring motors of today’s autonomous vehicles lies something far more revolutionary than fancy paint jobs and cup holders—artificial intelligence that’s fundamentally doing the job of a human driver, minus the road rage and questionable music choices.
This AI brain serves as the central nervous system, coordinating perception, decision-making, and control functions through an intricate web of algorithms and neural networks.
Imagine trying to process a dozen different sensory inputs while calculating trajectory physics and predicting what that erratic driver in the next lane might do—all while finding your way to the nearest Starbucks. That’s Tuesday for an autonomous vehicle’s AI.
Through deep learning, these systems interpret inputs from cameras, lidar, and radar to create a thorough 360-degree view of their surroundings, much like how you piece together your environment, just with fewer blind spots and no need for coffee breaks.
The real magic happens in the decision module, where AI weighs countless variables to determine whether to change lanes, adjust speed, or execute emergency maneuvers. AI must continually predict future events and make split-second decisions based on evolving road conditions.
Unlike your cousin who panics when merging onto highways, autonomous AI coolly calculates best paths while accounting for everything from traffic laws to social norms. Current vehicles in the market are only at level two automation or lower according to industry classification standards. It’s like having a Formula 1 driver, chess grandmaster, and safety inspector rolled into one digital package.
Control systems then translate these decisions into precise commands for steering, braking, and acceleration with millisecond accuracy.
The vehicle fundamentally becomes an extension of the AI’s digital mind, responding with reflexes that would make Olympic athletes jealous.
Before hitting public roads, these systems undergo rigorous testing in both virtual simulations and controlled environments.
Engineers throw everything from simulated snowstorms to virtual toddlers chasing balls into the street at these AI systems. It’s like driver’s ed on steroids—if your driving instructor could spawn random obstacles and rewind time.
As these technologies mature, they promise not just safer roads but also improved energy consumption and reduced environmental impact, proving that sometimes the smartest driver might not be human at all. Much like in cybersecurity, these systems employ sophisticated anomaly detection to identify unusual road conditions or potential hazards that could compromise vehicle safety.